Yearbook 1996
Costa Rica. Difficulties in meeting the International Monetary Fund’s demand for a budget deficit prompted President José María Figueres to reshape the government in early July. Some ministers changed ministries and new ones took up some posts. A consortium consisting of ABB Kraft, Norwegian Kværner and the construction company NCC’s Norwegian subsidiary Eeg-Henriksen received a building order from Costa Rica at the end of October regarding a hydroelectric power plant. The project is part of a larger climate project. The order amount was about SEK 270 million.
- ABBREVIATIONFINDER.ORG: What does CR stand for? In the field of geography, this two letter acronym means Costa Rica. Check this to see its other meanings in English and other 35 languages.
Country data
Area: 51,100 km2 (world ranking: 126)
Residents: 4,906,000
Population density: 96 per km2 (as of 2017, world ranking: 120)
Capital: San José
Official languages: Spanish
Gross domestic product: 57.1 billion US $; Real growth: 3.2%
Gross national product (GNP, per resident and year): 11,040 US$
Currency: 1 Costa Rican Colón (cent) = 100 Céntimos
Embassy
Reinhardtstr. 47 A, 10117 Berlin
Telephone 030 26398990,
Fax 030 26557210
www.botschaft-costarica.de
Government
Head of State and Government: Carlos Alvarado Quesada Epsy Campbell BarrMarvin Rodríguez Cordero
National holiday: 15.9.
Administrative divisions
7 provinces
Form of Government
Constitution of 1949
presidential
state religion: Catholicism
Parliament: Legislative Assembly (Asamblea Legislativa) with 57 Members Rank, elections every 4 years.
Direct election of the head of state every 4 years (no immediate re-election)
Elective over 18 years
Population: Costa Ricans, last census 2011: 4,301,712 residents 94% European, 3% African, 2% Asian, 1% indigenous
Cities (with population): (as of 2017, all A) San José 1,415,300 inh., Heredia 356,200, Cartago 227,500, Alajuela 189,900, Puntarenas 83,500
Religions: 73% Catholics, 15% Protestants; 8% without religion (as of 2006)
Languages: Spanish; English and Creole
workers according to the
agricultural sector. 12%, industry 19%, business 69% (2017)
Unemployment (in% of all labor force): 2017: 8.1%
Inflation rate (in%): 2017: 1.6%
Foreign trade: import: 15.5 billion US$ (2017); Export: 10.7 billion US $ (2017)
Climate
The relief creates three different climatic areas: In the north and north-east, the north-east trade wind brings intense rainfall and rainforest climate all year round. The interior is mild with temperatures between 19 and 21 ° C and rainfall of 230mm in July and 8mm in January. The west and southwest is alternately humid with a dry season lasting several months.
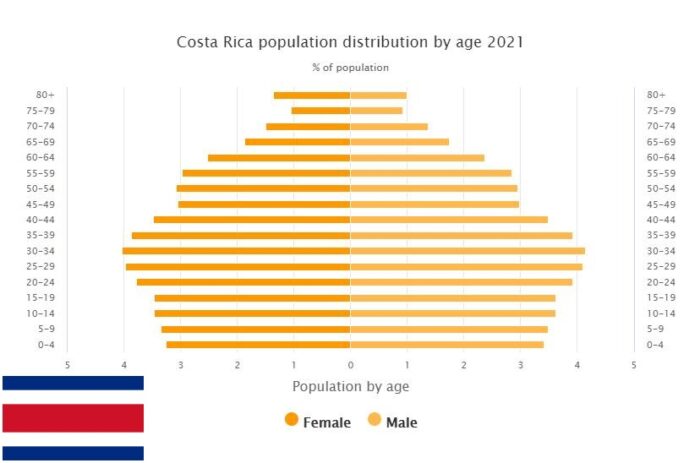
Population 1996
According to Countryaah.com, the population of Costa Rica in 1996 was 3,545,423, ranking number 124 in the world. The population growth rate was 2.590% yearly, and the population density was 69.4386 people per km2.
Population
The population is almost entirely of European origin and 88% are Catholic. Since the 1980s, the average annual growth rate has contracted and from a value of 27 ‰ it fell to 20 ‰ in the following decade and to 14 ‰ in 2008. The birth and death rates have also decreased, reaching the first on 17 ‰ and the second on 3.8 ‰; infant mortality also decreased, down to 9% (2008). On the other hand, the phenomenon of urbanization does not show subsidence and the urban population rate has now reached the threshold of 61%. From the point of view of demographic distribution, the opposition between the center of the country, the Meseta, and the sparsely populated outskirts of the mountains and the two opposite maritime sides is even more accentuated. Today the heart of the Meseta is occupied by a real urban region,2 hosts more than half of the national population: its nucleus is the capital, San José, and extends westward to Alajuela and eastward to Cartago, the ancient colonial capital.
Economic conditions
After a period of stagnation and uncertainty, linked above all to the strong dependence on international markets, the economy of C. has shown, since the early 1990s, a renewed vitality. Among the productive activities, agriculture plays a leading role; the most profitable crops are those of coffee, widespread in the central highlands, and bananas, grown in the plantations of the Caribbean coast. Among the industrial crops, or those destined for export, sugar cane and cocoa are relevant. For internal consumption, maize, rice, cassava and oil palm are grown. Fishing is quite profitable, in particular that of tuna, to which freezing and canning plants are connected. The energy sector is in progress, favored by numerous investments,
The Pan American Highway allows the connection with Nicaragua and Panama; the 1000 km of railway lines connect the maritime fronts of the country. The main ports are Limón (Caribbean Sea), Puntarenas, Golfito and Quepos (Pacific Ocean).